The following are flowcharts for the processing of common processed products made from carambola from the MARDI Food Technology Division, Malaysia.
Flowchart 2: Carambola beverage processing

Under normal storage conditions, the fine pulp in the cordial may settle at the bottom. The problem may be rectified with the addition of chmoxymethyl cellulose (CMC) as a stabiliser at a concentration of less than 0.1%.
All cordial batches should be uniform in colour. The addition of ß-carotene is useful for this purpose. The preferred container for cordials are glass bottles. The dullness of the cordial colour may be mitigated with sodium metabisulfite at the concentration of less than 80 ppm. Storage in a cool and dark place is recommended.
Flowchart 3: Carambola cordial processing

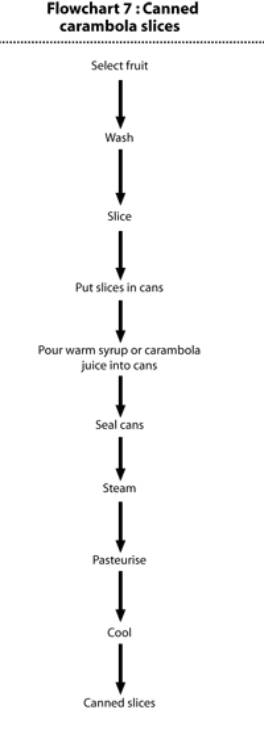
Flowchart 4: Carambola jam processing
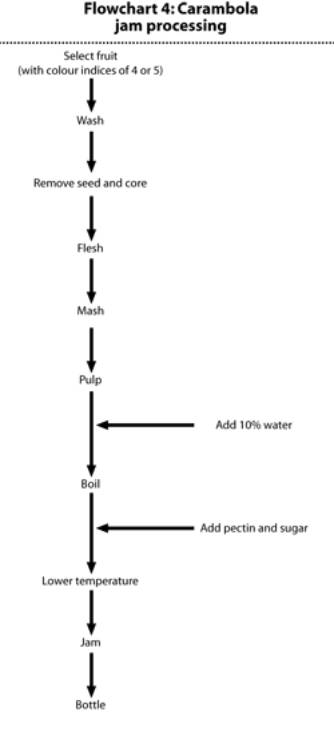
Flowchart 5: Confectionary jelly processing
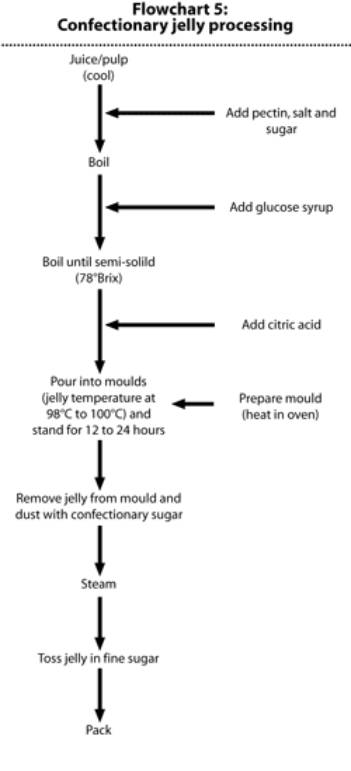
Flowchart 6: Dried carambola processing
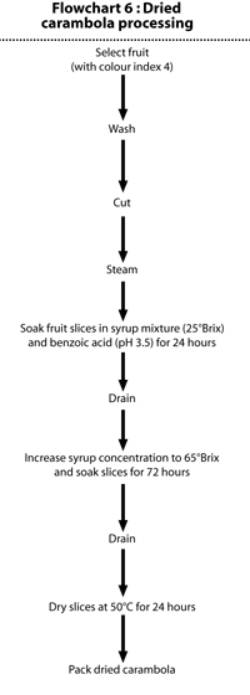
Flowchart 7: Canned carambola slices
All source come from: http://myfruits.mardi.my/main |

