| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
| |
|
| |
| Use the flesh of ripe rambutans. Rambutans may be canned in syrup alone or with other fruits like pineapple, jackfruit or starfruit. The fruits are placed into cans before being filled with syrup and then sealed. The concentration of the syrup is adjusted according to market requirements. Rambutan is usually canned as a high-acid food. |
| |
|
| |
Ripe, soft-textured rambutan is preferred for the making of rambutan jam. The jam should contain 35% fruit and 65% total soluble solids.
Pass rambutan flesh through a pulper. Then cook fruit pulp with pectin, sugar, acid and preservatives until the mixture reaches 65-68 ºBrix. Rambutan jam is bottled hot.
Rambutan pulp may be used alone or in combination with other fresh or semi-processed fruit pulps. |
| |
|
| |
Ripe, firm-textured rambutan flesh can be dehydrated.
Mix the dry rambutan flesh with sugar. Heat the mixture to remove moisture before drying. For a sweetened dehydrated product, soak and submerge the rambutan flesh in syrup. Increase the syrup concentration by 5 ºBrix daily until the desired sweetness is achieved. Drain the flesh and dehydrate it in a dehydrator at 45-50ºC until the pieces do not stick together. The flowchart for dehydrated rambutan processing is given in Flowchart 1.
Flow Chart 1: Dehydrated, Sweetened Rambutan Processing

|
| |
|
| |
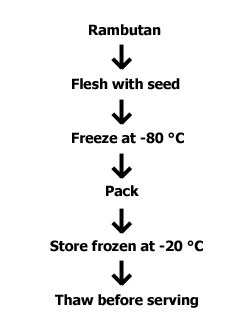
Ripe, firm textured rambutan can be frozen whole. Freeze the fruits, with its seed, by cryogenic freezing at -80 °C. Pack and store the frozen fruits at -20 °C. Thaw the fruits before serving. The frozen rambutan can be stored for 6 months. The flowchart for frozen rambutan processing is given in Flowchart 2.
Flow Chart 2: Frozen Rambutan Processing
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
| |
|
 |
 |
 |
| Names |
| |
|
|
|
Nepthelium lappaceum
|
|
|
Common: |
|
English: |
Rambutan |
Indonesia: |
Rambutan |
Malaysia: |
Rambutan |
Tagalog (Philippines): |
Rambutan |
Thai: |
Ngoh |
| Tamil: |
Rambutan |
Mandarin: |
Hongmaodan |
Vietnam: |
Choâm choâm |
Cambodian: |
Ser mon, Chle sao mao |
|
|
Taxonomic Position: |
| |
|
Domain: |
Eukaryota |
Kingdom: |
Viridiplantae |
Phylum: |
Spermatophyta |
| Subphylum: |
Angiospermae |
Class: |
Dicotyledonae |
Order: |
Sapindales |
Family: |
Sapindaceae |
| |
|
| Other Names Used: |
| |
| Nephelium chryseum |
| Nephelium sufferrugineum |
|
 |
 |
 |
|
| |
| |
|

